Introduction
Prospecting used to start with a swipe of the credit card for sales prospecting tools that were really just big databases—download a CSV, upload to a sequencer, hope for the best. But data decays fast (industry baselines commonly cite ~22.5% annually, with some B2B segments degrading far higher). Add manual handoffs and missed buying signals, and you get motion without meetings.
This guide explains the shift from static lists to AI‑activated prospecting: how the category evolved, where Apollo/ZoomInfo/Cognism fit, what “activability” means, and how AI agents (e.g., Topo) transform outcomes. You’ll leave with a pragmatic buyer’s checklist, a good‑better‑best decision framework, and a clear lens for choosing tools that build pipeline, not just spreadsheets.
The Old Paradigm — Prospecting Databases (What They Are & Why They Rose)
Definition & Core Use Cases
A prospecting database is a searchable catalog of companies and contacts with firmographic, technographic, and contact fields sales teams query to build lists for outbound. Typical data: company size, industry, location, tech stack, job titles, seniority, emails/phones, and sometimes intent overlays. Databases became standard because they delivered instant volume across a defined ICP and plugged easily into enrichment and sequencing.
Common workflow (old model):
Query database → 2) Export CSV → 3) Clean/enrich emails → 4) Upload to sequencer → 5) Send generic cadence → 6) Manually triage replies → 7) Hand‑update CRM.
Supporting details: enrichment add‑ons (email validation, phone append), rules for list freshness, and one‑off projects for territory/account mapping.
The Hidden Costs — Data Decay, Manual Ops, and Missed Timing
Data decay: Contact and company data naturally degrades—role changes, domains retire, orgs merge. Baseline estimates often cite ~22.5% annual decay, with certain B2B segments reporting much higher. The impact: bounces, poor match rates, and rising complaint risk.
Ops friction: Time sinks moving data between point tools (database → enrichment → sequencer → CRM) compound at scale. Reps context‑switch, ops builds duct‑tape workflows, and crucial fields go stale between steps.
Missed signals: Static exports ignore dynamic triggers (new funding, leadership changes, stack shifts, hiring waves). You contact after the window, not during it.
Quality vs. volume: Teams chase coverage, not context. Lists grow; reply quality falls. Sequencers become spray‑and‑pray machines; domains get burned.
What it feels like: a lot of motion, not many meetings.
The Current Leaders — Apollo, ZoomInfo, Cognism (Strengths & Limits)
What They Do Well
ZoomInfo: Breadth and depth of US data, with advanced org charts and intent overlays; strong for large teams that need coverage and data governance.
Apollo: Attractive pricing and a combined data + built‑in engagement stack, enabling lean teams to get from search to send quickly; popular with startups and SMBs.
Cognism: Known for GDPR‑first posture and highly validated phone numbers in Europe; strong for EMEA coverage and compliant dialing motions.
When each shines
ZoomInfo: Enterprise or upper mid‑market US‑heavy coverage; RevOps control and integrations matter most.
Apollo: Budget‑sensitive teams that want one vendor for data + sequencing without heavy admin overhead.
Cognism: EU‑first GTM, strict compliance requirements, and call‑heavy motions that depend on verified mobiles.
Quick comparison (editorial overview):
Platform | Data depth & coverage | Region strength | Built‑in engagement | Pricing posture | Best fit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
ZoomInfo | Very strong company/contact graph; intent & org charts | US | Add‑on tools; strong integrations | Premium/Enterprise | Large teams prioritizing coverage & governance |
Apollo | Good breadth at accessible price | US + growing EMEA | Native sequences, simple UI | Budget‑friendly | Startups/SMBs wanting data+send in one |
Cognism | High‑quality, phone‑verified contacts | Europe/UK | Dialing workflows, compliance features | Mid‑to‑premium | EMEA‑centric programs with call focus |
Note: Always validate against your ICP and primary regions; coverage varies by niche.
Where They Fall Short: “Activability”
Owning data ≠ getting meetings. The modern bottleneck is activability—how quickly and precisely you can convert records into contextual outreach across channels. Gaps typically include:
Real‑time signals: Most workflows still rely on static filters, not continuous listening (funding, tech changes, hiring, content engagement).
Orchestration: Moving from data → message → send → learn still spans multiple tools and manual QA.
Follow‑through: Sequencers send; humans must triage replies, update CRM, and nudge next steps. Opportunities leak.
The result: strong lists, average outcomes. The next era closes this gap.
The New Paradigm — From Data to Activation (AI‑Powered Prospecting Platforms)
What “Activability” Means
Activability is the ability of your stack to turn data into qualified conversations—autonomously and continuously. Instead of static records, you run an agentic loop:
Source accounts and contacts from multiple data pools
Enrich and validate in real time
Detect signals (events that justify outreach now)
Personalize with context (not fluff)
Orchestrate multichannel (email + LinkedIn; warm calls where relevant)
Handle replies (classification, routing, booking)
Sync CRM natively (no swivel‑chair)
Learn & optimize (copy, timing, channel, segment)
This is not a single feature; it’s a closed‑loop system where data and actions live together.
Old vs. New Lifecycle
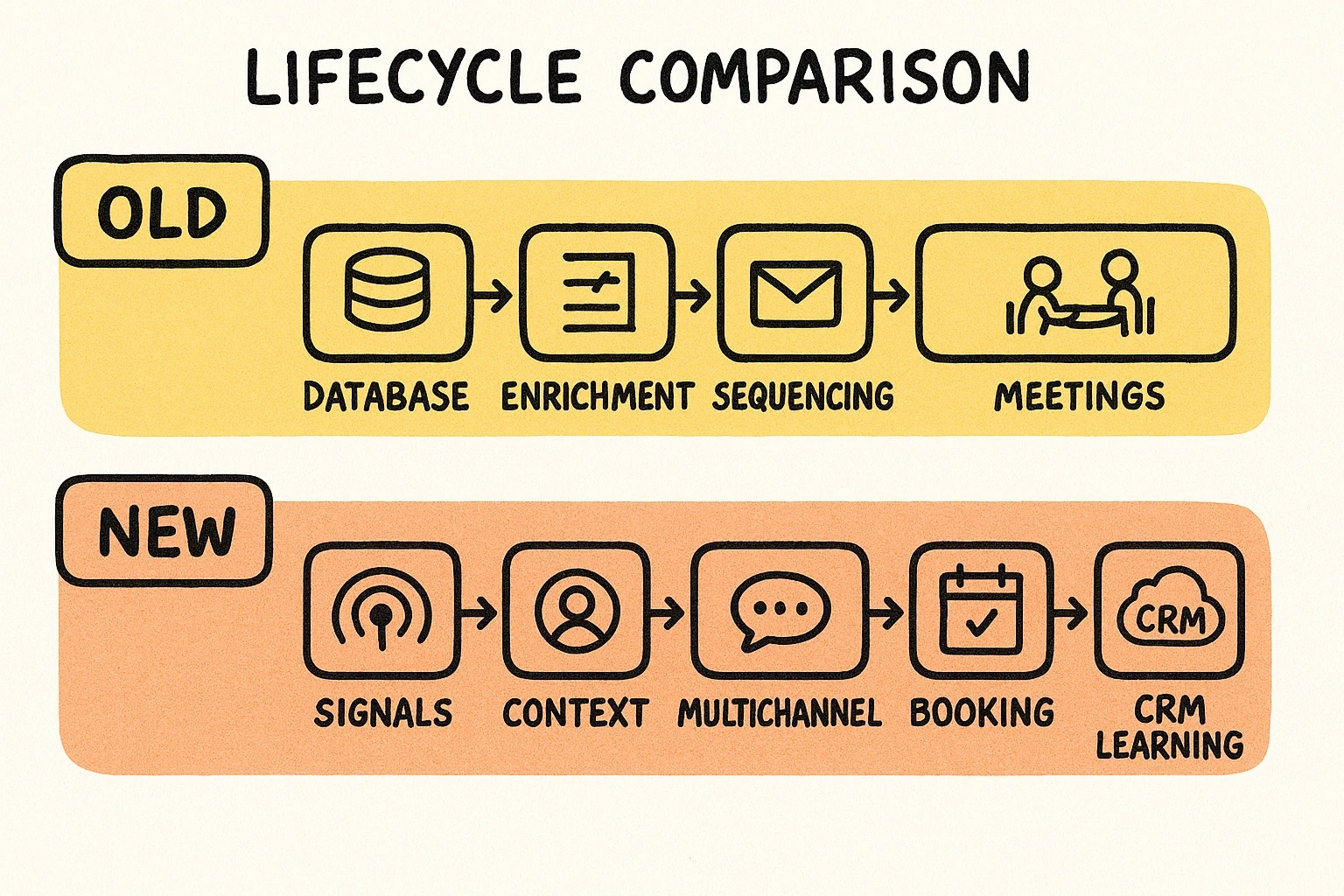
Market signals of the shift: Leading engagement vendors now ship AI prospecting agents, and buyers increasingly ask for outcomes (meetings booked, opportunity conversion) rather than raw contacts. The center of gravity moves from “who’s in the database” to “who’s ready, right now—and what do we do about it automatically?”
Capabilities Checklist for AI‑Activated Prospecting
Use this to evaluate platforms claiming “AI SDR” or agent features:
Signal detection: Funding, hiring, tech installs/changes, content/intent, product usage surges, competitive events.
Auto‑enrichment: Email validation, phone append, role verification at send‑time.
Channel orchestration: Email + LinkedIn by default; optional call assists; dynamic step switching on signal/reply.
Human‑in‑the‑loop: Lightweight review for new plays, messaging, and QA guardrails.
Deliverability infrastructure: Domain pools/warmup, reputation monitoring, list scrubbing, throttling, and premium inbox options when volume scales.
CRM‑native sync: Field‑level writes, dedupe, dispositioning, and attribution—no CSVs.
Learning loops: Auto‑experiments (subject lines, opens, reply reasons), cohort analysis, and next‑best‑action suggestions.
Governance & compliance: Role‑based controls, data residency, DNC/GDPR workflows, and audit trails.
Pricing transparency: Clear base + usage; cost per agent/seat/volume; realistic service/implementation needs.
Budget expectations: Teams typically reallocate database + sequencer + enrichment + infrastructure spend into an activation platform; net costs often resemble a “tool‑consolidation” line item while trading vanity metrics for booked meetings. Benchmark TCO using your current stack, domains, and headcount effort (ops + SDR time).
Case in Point — Topo and the AI‑Activated Stack
How AI SDRs Operate (and Why Hybrid > Fully Automated)
Topo’s model mirrors top SDR behavior with an AI agent + human strategist pairing:
Lead generation & enrichment: Agents source accounts/contacts from industry‑relevant sources; validate emails/phones on the fly.
Signal detection: Multi‑signal logic (e.g., hiring + product usage shifts + event attendance) to justify timing.
Contextual outreach: Short messages that cite the specific reason for contact—context over generic personalization.
Multichannel activation: Smart mixes of LinkedIn + email; warm calls when fit; adaptive sequencing.
Reply handling & booking: Automated triage with human oversight for tricky cases; calendar booking and CRM updates handled.
Reporting: Cohort‑level performance, reply reasons, and playbook insights.
Why hybrid wins: AI executes consistently at scale; humans provide creative plays, ICP nuance, and brand/tone judgment. The combo protects quality while compounding speed.
Outcomes & Proof
Teams replace manual research and fragmented tools with a focused activation loop:
From lists to meetings: Campaigns shift from volume plays to micro‑segments driven by signals, lifting reply quality and booked‑meeting rates.
Deliverability durability: Dedicated infrastructure and premium inbox strategies preserve domain reputation while scaling.
Ops simplicity: Fewer tools and fewer handoffs mean faster iteration and cleaner CRM data.
Teams running micro‑campaigns (stacked criteria with real‑time triggers) consistently see the back half of a test period outperform the front half—evidence that learning loops and message refinement matter. Quality scales when targeting sharpens.
How to Choose — Databases, Platforms, or AI Agents? (Decision Framework)
If You Need Data Only
Choose a database when:
You have a narrow ICP and a skilled team that can do deep manual research.
AEs are research‑heavy and prefer bespoke outreach.
You’re optimizing data coverage or QA for an existing, proven motion.
Where to store/manage: Start with a CRM that your team will actually maintain (there are credible free tiers for small teams) and enforce field hygiene from day one. Prioritize dedupe, role validation, and status reasons for every record.
If You Need Pipeline Fast
Choose activation‑first when:
Your priority is meetings now, not contacts later.
You need deep CRM sync, multi‑signal detection, deliverability controls, and agents that can run micro‑campaigns concurrently.
You’re consolidating tools and reducing ops overhead.
Good‑Better‑Best table
Level | What you buy | What you get | Trade‑offs |
Good | Database + manual research | Coverage; export lists | Slow to act; timing risk; ops overhead |
Better | Database + engagement platform | Faster send; basic automation | Still fragmented; limited signals; reply handling manual |
Best | AI agent platform (activation) | Signals → multichannel → booked meetings; CRM‑native | Requires initial playbook + guardrails; mindset shift to quality |
Buyer’s Checklist (Copy/Paste)
Use this 12‑point Activation Scorecard:
Intent/signal sources you can actually use (funding, hiring, tech shifts, event attendance, content/intent).
Custom signal logic (stacked triggers; timing windows).
Lead enrichment at send‑time (validation, phones, titles).
Sequencing & channel mix (email + LinkedIn; call assists; adaptive steps).
Reply handling (auto‑classification, routing, booking).
QA guardrails (human‑in‑the‑loop approvals; brand/voice controls).
Deliverability (domain pools, warmup, throttles, premium inboxes, suppression).
Data residency & compliance (GDPR, DNC, audit trails).
CRM‑native sync (field mapping, dedupe, attribution).
Learning loops (auto‑experiments, performance by segment, next‑best‑action).
Pricing transparency (base + usage, infra costs, services clearly scoped).
Outcome reporting (meetings booked, reply quality, oppty conversion), not vanity opens/clicks.
Conclusion
Databases are table stakes; activation is the advantage. The shift from static lists to AI‑driven, signal‑based outreach rewards teams that value quality over quantity and systems over hacks. Start with a clear ICP and plays, then select tools that execute the loop—source → enrich → signal → orchestrate → book → learn—without breaking your ops.
Next steps: Copy the 12‑point checklist into your evaluation doc, run a micro‑campaign pilot with a narrow ICP + clear signal, and measure meetings‑to‑opportunities—not clicks. If you want a north‑star example of hybrid agents in action, study how AI SDRs are paired with human strategy to turn context into conversations.
Introduction
Prospecting used to start with a swipe of the credit card for sales prospecting tools that were really just big databases—download a CSV, upload to a sequencer, hope for the best. But data decays fast (industry baselines commonly cite ~22.5% annually, with some B2B segments degrading far higher). Add manual handoffs and missed buying signals, and you get motion without meetings.
This guide explains the shift from static lists to AI‑activated prospecting: how the category evolved, where Apollo/ZoomInfo/Cognism fit, what “activability” means, and how AI agents (e.g., Topo) transform outcomes. You’ll leave with a pragmatic buyer’s checklist, a good‑better‑best decision framework, and a clear lens for choosing tools that build pipeline, not just spreadsheets.
The Old Paradigm — Prospecting Databases (What They Are & Why They Rose)
Definition & Core Use Cases
A prospecting database is a searchable catalog of companies and contacts with firmographic, technographic, and contact fields sales teams query to build lists for outbound. Typical data: company size, industry, location, tech stack, job titles, seniority, emails/phones, and sometimes intent overlays. Databases became standard because they delivered instant volume across a defined ICP and plugged easily into enrichment and sequencing.
Common workflow (old model):
Query database → 2) Export CSV → 3) Clean/enrich emails → 4) Upload to sequencer → 5) Send generic cadence → 6) Manually triage replies → 7) Hand‑update CRM.
Supporting details: enrichment add‑ons (email validation, phone append), rules for list freshness, and one‑off projects for territory/account mapping.
The Hidden Costs — Data Decay, Manual Ops, and Missed Timing
Data decay: Contact and company data naturally degrades—role changes, domains retire, orgs merge. Baseline estimates often cite ~22.5% annual decay, with certain B2B segments reporting much higher. The impact: bounces, poor match rates, and rising complaint risk.
Ops friction: Time sinks moving data between point tools (database → enrichment → sequencer → CRM) compound at scale. Reps context‑switch, ops builds duct‑tape workflows, and crucial fields go stale between steps.
Missed signals: Static exports ignore dynamic triggers (new funding, leadership changes, stack shifts, hiring waves). You contact after the window, not during it.
Quality vs. volume: Teams chase coverage, not context. Lists grow; reply quality falls. Sequencers become spray‑and‑pray machines; domains get burned.
What it feels like: a lot of motion, not many meetings.
The Current Leaders — Apollo, ZoomInfo, Cognism (Strengths & Limits)
What They Do Well
ZoomInfo: Breadth and depth of US data, with advanced org charts and intent overlays; strong for large teams that need coverage and data governance.
Apollo: Attractive pricing and a combined data + built‑in engagement stack, enabling lean teams to get from search to send quickly; popular with startups and SMBs.
Cognism: Known for GDPR‑first posture and highly validated phone numbers in Europe; strong for EMEA coverage and compliant dialing motions.
When each shines
ZoomInfo: Enterprise or upper mid‑market US‑heavy coverage; RevOps control and integrations matter most.
Apollo: Budget‑sensitive teams that want one vendor for data + sequencing without heavy admin overhead.
Cognism: EU‑first GTM, strict compliance requirements, and call‑heavy motions that depend on verified mobiles.
Quick comparison (editorial overview):
Platform | Data depth & coverage | Region strength | Built‑in engagement | Pricing posture | Best fit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
ZoomInfo | Very strong company/contact graph; intent & org charts | US | Add‑on tools; strong integrations | Premium/Enterprise | Large teams prioritizing coverage & governance |
Apollo | Good breadth at accessible price | US + growing EMEA | Native sequences, simple UI | Budget‑friendly | Startups/SMBs wanting data+send in one |
Cognism | High‑quality, phone‑verified contacts | Europe/UK | Dialing workflows, compliance features | Mid‑to‑premium | EMEA‑centric programs with call focus |
Note: Always validate against your ICP and primary regions; coverage varies by niche.
Where They Fall Short: “Activability”
Owning data ≠ getting meetings. The modern bottleneck is activability—how quickly and precisely you can convert records into contextual outreach across channels. Gaps typically include:
Real‑time signals: Most workflows still rely on static filters, not continuous listening (funding, tech changes, hiring, content engagement).
Orchestration: Moving from data → message → send → learn still spans multiple tools and manual QA.
Follow‑through: Sequencers send; humans must triage replies, update CRM, and nudge next steps. Opportunities leak.
The result: strong lists, average outcomes. The next era closes this gap.
The New Paradigm — From Data to Activation (AI‑Powered Prospecting Platforms)
What “Activability” Means
Activability is the ability of your stack to turn data into qualified conversations—autonomously and continuously. Instead of static records, you run an agentic loop:
Source accounts and contacts from multiple data pools
Enrich and validate in real time
Detect signals (events that justify outreach now)
Personalize with context (not fluff)
Orchestrate multichannel (email + LinkedIn; warm calls where relevant)
Handle replies (classification, routing, booking)
Sync CRM natively (no swivel‑chair)
Learn & optimize (copy, timing, channel, segment)
This is not a single feature; it’s a closed‑loop system where data and actions live together.
Old vs. New Lifecycle

Market signals of the shift: Leading engagement vendors now ship AI prospecting agents, and buyers increasingly ask for outcomes (meetings booked, opportunity conversion) rather than raw contacts. The center of gravity moves from “who’s in the database” to “who’s ready, right now—and what do we do about it automatically?”
Capabilities Checklist for AI‑Activated Prospecting
Use this to evaluate platforms claiming “AI SDR” or agent features:
Signal detection: Funding, hiring, tech installs/changes, content/intent, product usage surges, competitive events.
Auto‑enrichment: Email validation, phone append, role verification at send‑time.
Channel orchestration: Email + LinkedIn by default; optional call assists; dynamic step switching on signal/reply.
Human‑in‑the‑loop: Lightweight review for new plays, messaging, and QA guardrails.
Deliverability infrastructure: Domain pools/warmup, reputation monitoring, list scrubbing, throttling, and premium inbox options when volume scales.
CRM‑native sync: Field‑level writes, dedupe, dispositioning, and attribution—no CSVs.
Learning loops: Auto‑experiments (subject lines, opens, reply reasons), cohort analysis, and next‑best‑action suggestions.
Governance & compliance: Role‑based controls, data residency, DNC/GDPR workflows, and audit trails.
Pricing transparency: Clear base + usage; cost per agent/seat/volume; realistic service/implementation needs.
Budget expectations: Teams typically reallocate database + sequencer + enrichment + infrastructure spend into an activation platform; net costs often resemble a “tool‑consolidation” line item while trading vanity metrics for booked meetings. Benchmark TCO using your current stack, domains, and headcount effort (ops + SDR time).
Case in Point — Topo and the AI‑Activated Stack
How AI SDRs Operate (and Why Hybrid > Fully Automated)
Topo’s model mirrors top SDR behavior with an AI agent + human strategist pairing:
Lead generation & enrichment: Agents source accounts/contacts from industry‑relevant sources; validate emails/phones on the fly.
Signal detection: Multi‑signal logic (e.g., hiring + product usage shifts + event attendance) to justify timing.
Contextual outreach: Short messages that cite the specific reason for contact—context over generic personalization.
Multichannel activation: Smart mixes of LinkedIn + email; warm calls when fit; adaptive sequencing.
Reply handling & booking: Automated triage with human oversight for tricky cases; calendar booking and CRM updates handled.
Reporting: Cohort‑level performance, reply reasons, and playbook insights.
Why hybrid wins: AI executes consistently at scale; humans provide creative plays, ICP nuance, and brand/tone judgment. The combo protects quality while compounding speed.
Outcomes & Proof
Teams replace manual research and fragmented tools with a focused activation loop:
From lists to meetings: Campaigns shift from volume plays to micro‑segments driven by signals, lifting reply quality and booked‑meeting rates.
Deliverability durability: Dedicated infrastructure and premium inbox strategies preserve domain reputation while scaling.
Ops simplicity: Fewer tools and fewer handoffs mean faster iteration and cleaner CRM data.
Teams running micro‑campaigns (stacked criteria with real‑time triggers) consistently see the back half of a test period outperform the front half—evidence that learning loops and message refinement matter. Quality scales when targeting sharpens.
How to Choose — Databases, Platforms, or AI Agents? (Decision Framework)
If You Need Data Only
Choose a database when:
You have a narrow ICP and a skilled team that can do deep manual research.
AEs are research‑heavy and prefer bespoke outreach.
You’re optimizing data coverage or QA for an existing, proven motion.
Where to store/manage: Start with a CRM that your team will actually maintain (there are credible free tiers for small teams) and enforce field hygiene from day one. Prioritize dedupe, role validation, and status reasons for every record.
If You Need Pipeline Fast
Choose activation‑first when:
Your priority is meetings now, not contacts later.
You need deep CRM sync, multi‑signal detection, deliverability controls, and agents that can run micro‑campaigns concurrently.
You’re consolidating tools and reducing ops overhead.
Good‑Better‑Best table
Level | What you buy | What you get | Trade‑offs |
Good | Database + manual research | Coverage; export lists | Slow to act; timing risk; ops overhead |
Better | Database + engagement platform | Faster send; basic automation | Still fragmented; limited signals; reply handling manual |
Best | AI agent platform (activation) | Signals → multichannel → booked meetings; CRM‑native | Requires initial playbook + guardrails; mindset shift to quality |
Buyer’s Checklist (Copy/Paste)
Use this 12‑point Activation Scorecard:
Intent/signal sources you can actually use (funding, hiring, tech shifts, event attendance, content/intent).
Custom signal logic (stacked triggers; timing windows).
Lead enrichment at send‑time (validation, phones, titles).
Sequencing & channel mix (email + LinkedIn; call assists; adaptive steps).
Reply handling (auto‑classification, routing, booking).
QA guardrails (human‑in‑the‑loop approvals; brand/voice controls).
Deliverability (domain pools, warmup, throttles, premium inboxes, suppression).
Data residency & compliance (GDPR, DNC, audit trails).
CRM‑native sync (field mapping, dedupe, attribution).
Learning loops (auto‑experiments, performance by segment, next‑best‑action).
Pricing transparency (base + usage, infra costs, services clearly scoped).
Outcome reporting (meetings booked, reply quality, oppty conversion), not vanity opens/clicks.
Conclusion
Databases are table stakes; activation is the advantage. The shift from static lists to AI‑driven, signal‑based outreach rewards teams that value quality over quantity and systems over hacks. Start with a clear ICP and plays, then select tools that execute the loop—source → enrich → signal → orchestrate → book → learn—without breaking your ops.
Next steps: Copy the 12‑point checklist into your evaluation doc, run a micro‑campaign pilot with a narrow ICP + clear signal, and measure meetings‑to‑opportunities—not clicks. If you want a north‑star example of hybrid agents in action, study how AI SDRs are paired with human strategy to turn context into conversations.
FAQ
Which is best for EU vs. US data (Apollo, ZoomInfo, Cognism)?
If you need deep US coverage at scale, ZoomInfo is commonly favored. For budget‑friendly US coverage with built‑in engagement, Apollo is popular. For EU/UK compliance and validated phone numbers, Cognism is frequently selected. Always validate on a sample from your exact ICP and regions.
What’s the difference between a prospecting database and prospecting software?
A database is the raw catalog of companies/contacts; prospecting software includes the workflow to act on that data—finding, enriching, messaging, routing, and learning. Many teams once stitched these together manually; modern prospecting platforms combine data + action in one loop.
How often should I refresh my database to fight decay?
Plan for continuous enrichment. As a rule of thumb, if you’re exporting CSVs weekly, you’re already stale. Use send‑time validation and role checks; re‑verify high‑value segments monthly; and trigger refresh on detected events (title change, domain bounce, hiring surge).
Are there free prospecting tools or CRMs worth starting with?
Pros/cons. Yes—several CRMs have robust free tiers and lightweight prospecting features. Pros: low cost, fast time‑to‑value. Cons: limited governance, fewer automation hooks, and potential migration work later. Start lean; keep your data model clean.
Sources and references
Topo editorial line asks its authors to use sources to support their work. These can include original reporting, articles, white papers, product data, benchmarks and interviews with industry experts. We prioritize primary sources and authoritative references to ensure accuracy and credibility in all content related to B2B marketing, lead generation, and sales strategies.
Sources and references for this article
Sources and references
Topo editorial line asks its authors to use sources to support their work. These can include original reporting, articles, white papers, product data, benchmarks and interviews with industry experts. We prioritize primary sources and authoritative references to ensure accuracy and credibility in all content related to B2B marketing, lead generation, and sales strategies.
Sources and references for this article



